本文最后更新于:2024年5月7日 下午
最小二乘法则是一种统计学习优化技术,它的目标是最小化误差平方之和来作为目标,从而找到最优模型。
简介
最小二乘法则是一种统计学习优化技术,它的目标是最小化误差平方之和来作为目标 $J(θ)$,从而找到最优模型的方法,该误差目标定义为:
$$ J(\theta)=\min \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(f\left(x_{i}\right)-y_{i}\right)^{2} $$Scipy 对优化最小二乘 Loss 的方法做了一些封装,主要有 scipy.linalg.lstsq 和 scipy.optimize.leastsq 两种,此外还有 scipy.optimize.curve_fit 也可以用于拟合最小二乘参数。
scipy.linalg.lstsq
SciPy 的 linalg 下的 lstsq 着重解决传统、标准的最小二乘拟合问题,该方法限制了模型 $f(x_i)$的形式必须为 $ f\left(x_{i}\right)=a_{0}+a_{1} x^{1}+a_{2} x^{2}+\cdots+a^{n} x^{n} $ ,对于此类型的模型,给定模型和足够多的观测值 $ y_{i} $ 即可进行求解。
-
求解时需要将模型 $f(x_i)$ 改写成矩阵形式,矩阵用字母 $A $ 表示,则只需给出方程 $ f\left(x_{i}\right) $ 的模型即 $A$ 及样本 $ y_{i} $ 便可求得方程的各个系数。
-
函数调用方法:
1 | |
使用示例
例一
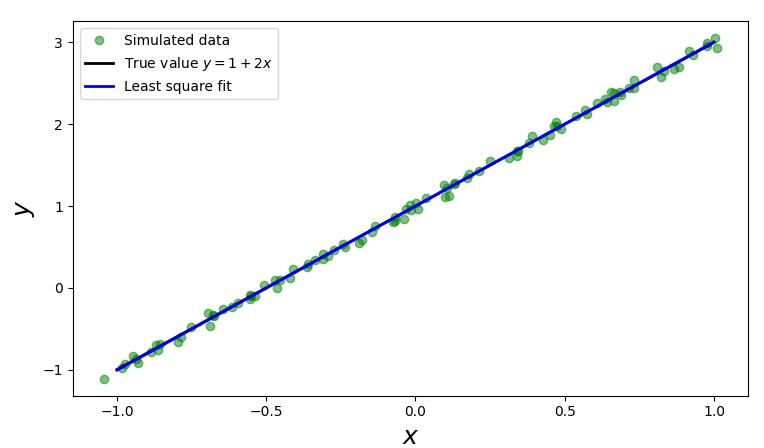
假设真实的模型是 $y=2x+1$,我们有一组数据 $(x_i,y_i)$ 共 100 个,看能否基于这 100 个数据找出 $x_i$
和 $ y_{i} $ 的线性关系方程 $ y=2 x+1 $ ,我们可以通过以下几步来完成。
- 序构造出100个 $(x_i,y_i)$ 数据。
1 | |
- 给出模型 $ f(x)=a+b x $ 的矩阵A。由于有100个观测 $ \left(x_{i}, y_{i}\right) $ 的数据,那么就有:
将以上式子写成如下矩阵的形式:
$$ \left|\begin{array}{cc}1 & x_{0} \\ 1 & x_{1} \\ \vdots & \vdots \\ 1 & x_{99}\end{array}\right| \times\left|\begin{array}{l}a \\ b\end{array}\right|=\left|\begin{array}{c}y_{0} \\ y_{1} \\ \vdots \\ y_{99}\end{array}\right| $$1 | |
- 调用
scipy.linalg.lstsq传入 $ A^{T} $ 和观测值里的 $ y_{i} $ 即程序里的yi变量即可求得 $ f(x)=a+b x $ 里的 $a$ 和 $b$。$a$ 和 $b$ 记录在 $Istsq$ 函数的第一个返回值里。
1 | |
scipy.linalg.Istsq的第一个返回值sol共有两个值,sol[0]即是估计出来的 $ f(x)=a+b x $ 里的 $a$, $ \operatorname{sol}[1] $ 代表 $ f(x)=a+b x $ 里的 $b$。因此 $ f(x) $ 为:
1 | |
-
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23import numpy
import scipy.linalg as la
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
m = 100
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, m)
y_exact = 1 + 2 * x
xi = x + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, 100)
yi = 1 + 2 * xi + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, 100)
print (xi,"#xi")
print (yi,"#yi")
A = np.vstack([xi**0, xi**1])
sol, r, rank, s = la.lstsq(A.T, yi)
y_fit = sol[0] + sol[1] * x
print (sol,r ,rank,s )
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
ax.plot(xi, yi, 'go', alpha=0.5, label='Simulated data')
ax.plot(x, y_exact, 'k', lw=2, label='True value $y = 1 + 2x$')
ax.plot(x, y_fit, 'b', lw=2, label='Least square fit')
ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$", fontsize=18)
ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$", fontsize=18)
ax.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
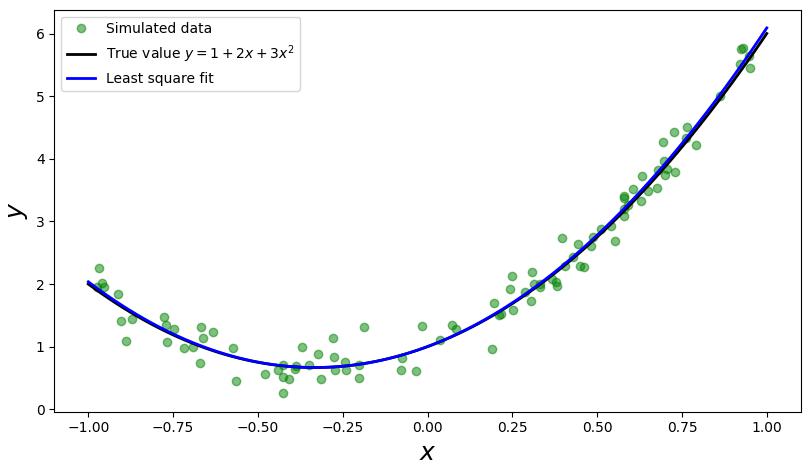
例二
考虑模型为 $f\left(x_{i}\right)=a+b x+c x^{2} $ 的情况:
-
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23import numpy
import scipy.linalg as la
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)
a, b, c = 1, 2, 3
y_exact = a + b * x + c * x**2
m = 100
xi=1 - 2 * np.random.rand(m)
print ("xi.shape", xi.shape,xi**1,xi)
yi=a + b * xi + c * xi**2 + np.random.randn(m) * 0.2
A = np.vstack([xi**0, xi**1, xi**2])
print (A.shape, A.T.shape)
sol, r, rank, s = la.lstsq(A.T, yi)
y_fit = sol[0] + sol[1] * x + sol[2] * x**2
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 4))
ax.plot(xi, yi, 'go', alpha=0.5, label='Simulated data')
ax.plot(x, y_exact, 'k', lw=2, label='True value $y = 1 + 2x + 3x^2$')
ax.plot(x, y_fit, 'b', lw=2, label='Least square fit')
ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$", fontsize=18)
ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$", fontsize=18)
ax.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
scipy.optimize.leastsq
scipy.optimize.leastsq 方法相比于 scipy.linalg.lstsq 更加灵活,开放了 $f(x_i)$ 的模型形式。
leastsq() 函数传入误差计算函数和初始值,该初始值将作为误差计算函数的第一个参数传入。计算的结果是一个包含两个元素的元组,第一个元素是一个数组,表示拟合后的参数;第二个元素如果等于1、2、3、4中的其中一个整数,则拟合成功,否则将会返回 mesg。
调用示例
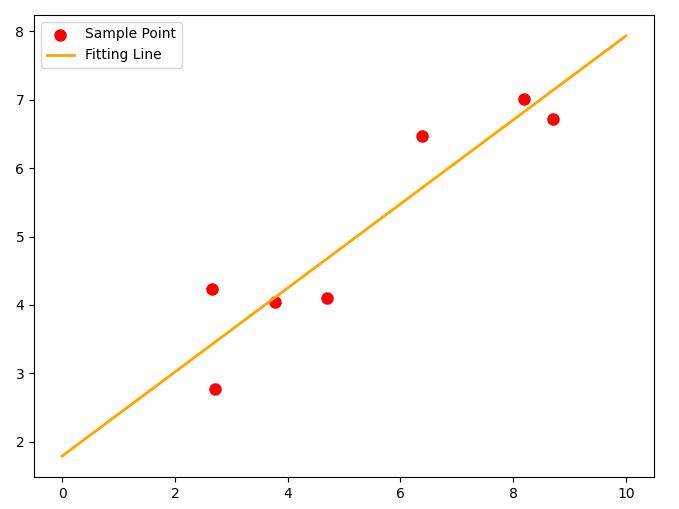
例一
首先仍以线性拟合为例,拟合 $ f(x)=a x+b $ 函数。
- 示例代码
1 | |
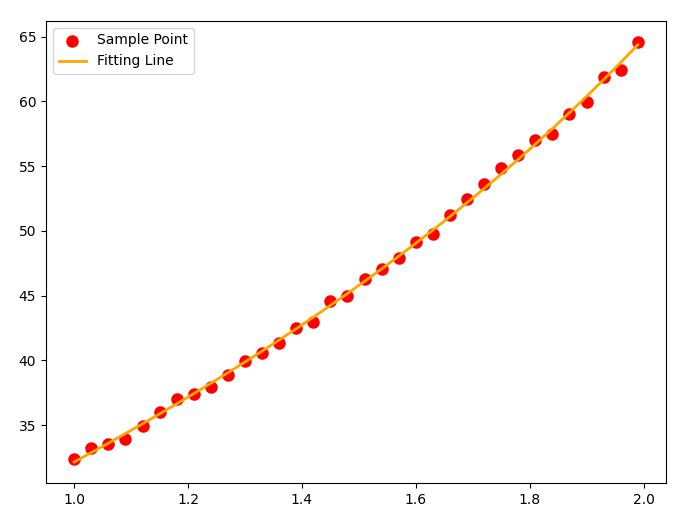
例二
这里我们展现一下 leastsq 的灵活之处,由于 leastsq 放开了对 $f(x_i)$ 形式的严格限制,我们可以设置一些更加复杂的最小二乘的情况。
例如我现在就要拟合这么个函数:
$$
f(x)=7e^x+3\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+12\sin x
$$
相比于之前的多项式函数可以说有些丧心病狂了,但是也是在 leastsq 射程范围内:
1 | |
核心函数:
1 | |
- 其中:
err为用于计算残差的 Callback 函数,p0为初始解,args为输入的数据。
输出结果:
1 | |
优化方法不是万能的,如果矩阵过于奇异,也是不利于准确求解模型参数的。
scipy.optimize.curve_fit
scipy.optimize.curve_fit 函数用于拟合曲线,给出模型和数据就可以拟合,相比于 leastsq 来说使用起来方便的地方在于不需要输入初始值。
1 | |
其中 fun 为输入参数为 $x$ 和模型参数列表,输出 $y$ 的 Callback 函数,$X$ 和 $Y$ 为数据
调用示例
例一
为了方便对比,将上文例二的示例代码修改成
curve_fit函数的实现
- 示例代码:
1 | |
输出结果:
1 | |
绘制图像:
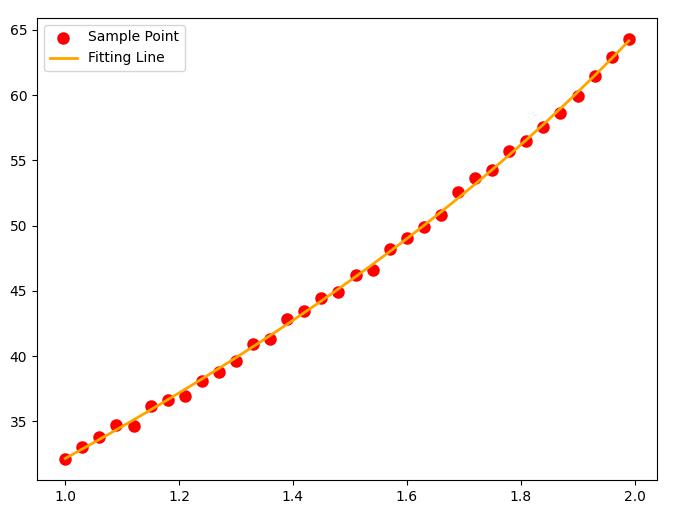
效果没有
leastsq稳定,可能是没有初始值的缘故。
参考资料
- http://liao.cpython.org/scipy07.html
- https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.linalg.lstsq.html#scipy.linalg.lstsq
- https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.leastsq.html
- https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.curve_fit.html#scipy.optimize.curve_fit
- http://liao.cpython.org/scipytutorial07.html#7-scipy-tutorial-
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/72241280
- https://huhuhang.com/post/machine-learning/scipy-optimize-leastsq
- https://hg95.github.io/numpy-pandas-scipy/Chapter3/拟合与优化optimize/最小二乘法拟合leastsq.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/sunbright/article/details/24717963
- http://python.circuitpython.cn/scipy05/index.html
文章链接:
https://www.zywvvd.com/notes/coding/python/scipy-leastsquare/scipy-leastsquare/
“觉得不错的话,给点打赏吧 ୧(๑•̀⌄•́๑)૭”

微信支付
支付宝支付