本文最后更新于:2025年5月13日 晚上
透视 n 点问题,简称 PnP,源自相机标定,是计算机视觉的经典问题,广泛应用在机器人定位、SLAM、AR/VR、摄影测量等领域。
问题定义
已知:相机的内参和畸变系数;世界坐标系中,n 个空间点坐标,以及投影在像平面上的像素坐标
求解:相机在世界坐标系下的位姿 R 和 t,即 {W} 到 {C} 的变换矩阵 $^w_cT$,如下图:
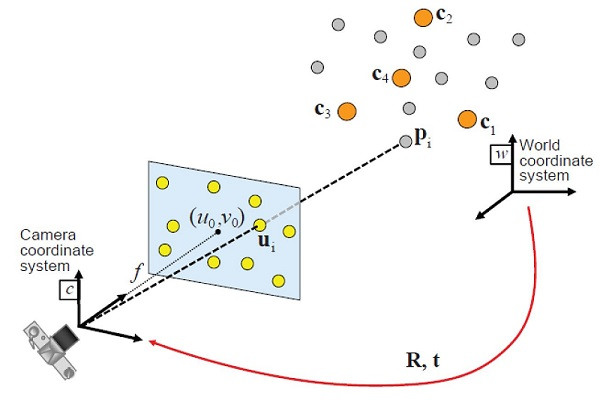
世界坐标系中的 3d 空间点,与投影到像平面的 2d 像素点,两者之间的关系为:
$$ s\begin{bmatrix}u\\v\\1\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}f_x&0&c_x\\0&f_y&c_y\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}r_{11}&r_{12}&r_{13}&t_1\\r_{21}&r_{22}&r_{23}&t_2\\r_{31}&r_{32}&r_{33}&t_3\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}X_w\\Y_w\\Z_w\\1\end{bmatrix} $$分类
根据给定空间点的数量,可将 PnP 问题分为两类:
-
第一类 $3≤n≤5$,选取的空间点较少,可通过联立方程组的方式求解,精度易受图像噪声影响,鲁棒性较差
-
第二类 $n≥6$,选取的空间点较多,可转化为求解超定方程的问题,一般侧重于鲁棒性和实时性的平衡
DLT 法
转化为 Ax=0
令 $𝑃=𝐾[𝑅𝑡]$,$K$ 为相机内参矩阵,则 PnP 问题可简化为:已知 n 组 3d-2d 对应点,求解 $P_{3×4}$
DLT (Direct Linear Transformation,直接线性变换),便是直接利用这 n 组对应点,构建线性方程组来求解
$$ s\begin{bmatrix}u\\v\\1\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}p_{11}&p_{12}&p_{13}&p_{14}\\p_{21}&p_{22}&p_{23}&p_{23}\\p_{31}&p_{32}&p_{33}&p_{33}\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}X_w\\Y_w\\Z_w\\1\end{bmatrix} $$简化符号 $X_w,Y_w,Z_w$ 为 $X,Y,Z$,展开得:
$$ \left.\left\{\begin{array}{l}su=p_{11}X+p_{12}Y+p_{13}Z+p_{14}\\\\sv=p_{21}X+p_{22}Y+p_{23}Z+p_{24}\\\\s=p_{31}X+p_{32}Y+p_{33}Z+p_{34}\end{array}\right.\right.=>\left\{\begin{array}{l}Xp_{11}+Yp_{12}+Zp_{13}+p_{14}-uXp_{31}-uYp_{32}-uZp_{33}-up_{34}=0\\\\Xp_{21}+Yp_{22}+Zp_{23}+p_{24}-vXp_{31}-vYp_{32}-vZp_{33}-vp_{34}=0\end{array}\right. $$未知数有 11 个 ($p_{34}$可约掉),则至少需要 6 组对应点,写成矩阵形式如下:
$$ \begin{bmatrix}X_1&Y_1&Z_1&1&0&0&0&0&-u_1X_1&-u_1Y_1&-u_1Z_1&-u_1\\0&0&0&0&X_1&Y_1&Z_1&1&-v_1X_1&-v_1Y_1&-v_1Z_1&-v_1\\\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots\\\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots\\X_n&Y_n&Z_n&1&0&0&0&0&-u_nX_n&-u_nY_1&-u_nZ_n&-u_n\\0&0&0&0&X_n&Y_n&Z_n&1&-v_nX_n&-v_nY_n&-v_nZ_n&-v_n\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}p_{11}\\p_{12}\\p_{13}\\p_{14}\\\vdots\\p_{32}\\p_{33}\\p_{34}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}0\\\vdots\\\vdots\\\vdots\\0\end{bmatrix} $$因此,求解 $𝑃_{3×4}$ 便转化成了 $Ax=0$ 的问题
SVD 求 R t
给定相机内参矩阵 $K$,则有 $K[R|t]=λ[p_1 \text{ }p_2 \text{ }p_3\text{ }p_4]$
考虑 $λ$ 符号无关,得 $𝜆𝑅=𝐾^{−1}[𝑝_1\text{ }𝑝_2\text{ }𝑝_3]$
SVD 分解:
$$ K^{-1}\left[\begin{matrix}p_1&p_2&p_3\end{matrix}\right]=\boldsymbol{U}\begin{bmatrix}d_{11}&&&\\&d_{22}&&\\&&&d_{33}\end{bmatrix}\boldsymbol{V}^T $$ 得到: $$ \lambda\approx d_{11}\text{ 和 }\begin{cases}R=UV^T\\t=\frac{K^{-1}p_4}{d_{11}}\end{cases} $$P3P 法
当 n=3 时,PnP 即为 P3P,它有 4 个可能的解,求解方法是 余弦定理 + 向量点积
余弦定理
根据投影几何的消隐点和消隐线,构建 3d-2d 之间的几何关系,如下:
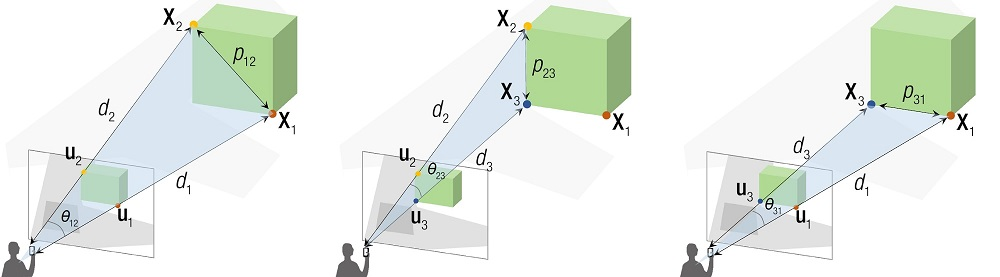
根据余弦定理,有:
$$ \left.\left\{\begin{array}{l}d_1^2+d_2^2-2d_1d_2\cos\theta_{12}=p_{12}^2\\\\d_2^2+d_3^2-2d_2d_3\cos\theta_{23}=p_{23}^2\\\\d_3^2+d_1^2+2d_3d_2\cos\theta_23=p_{31}^2\end{array}\right.\right. $$只有 $d_1,d_2,d_3$ 是未知数,求解方程组即可
其中,有个关键的隐含点:给定相机内参,以及 3d-2d 的投影关系,则消隐线之间的夹角 $θ_{12}\text{ }θ_{23}\text{ }θ_{31}$ 是可计算得出的
向量点积
相机坐标系中,原点即为消隐点,原点到 3d-2d 的连线即为消隐线,如图所示:

如果知道 3d点 投影到像平面的 2d点,在相机坐标系中的坐标 $U_1,U_2,U_3$,则:
$$ \cos\theta_{23}=\frac{\overrightarrow{OU_{2}}\cdot\overrightarrow{OU_{3}}}{||\overrightarrow{OU_{2}}|| ||\overrightarrow{OU_{3}}||} $$具体到运算,可视为 世界坐标系 {W} 和 相机坐标系 {C} 重合,且 $Z=f$,则有:
$$ [ R\quad t ]=\begin{bmatrix}1&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0\\0&0&1&0\end{bmatrix}=> s\begin{bmatrix}u\\v\\1\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}f_x&0&c_x\\0&f_y&c_y\\0&0&1\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}X_c\\Y_c\\Z_c\end{bmatrix} $$$K^{−1}$ 可用增广矩阵求得,且 $Z_c=f$,则有:
$$ \begin{bmatrix}X_c\\Y_c\\f\end{bmatrix}=sK^{-1}\begin{bmatrix}u\\v\\1\end{bmatrix} $$ 记 $\vec{u}=\begin{bmatrix}X_c\\Y_c\\Z_c\end{bmatrix}$ , 则: $$ \cos\theta_{12}=\frac{(K^{-1}\vec{u_1})^T(K^{-1}\vec{u_2})}{||K^{-1}\vec{u_1}|| ||K^{-1}\vec{u_2}||} $$以此类推 $\cos\theta_{23}$ 和 $\cos\theta_{31}$
OpenCV 实现
OpenCV 中解 PnP 的方法有 9 种,目前实现了 7 种,还有 2 种未实现,对应论文如下:
-
SOLVEPNP_P3P Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem
-
SOLVEPNP_AP3P An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem
-
SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE 基于 L-M 最优化方法,求解重投影误差最小的位姿
-
SOLVEPNP_EPNP EPnP: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the PnP Problem
-
SOLVEPNP_SQPNP A Consistently Fast and Globally Optimal Solution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem
-
SOLVEPNP_IPPE Infinitesimal Plane-based Pose Estimation 输入的 3D 点需要共面且 n ≥ 4
-
SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE SOLVEPNP_IPPE 的一种特殊情况,要求输入 4 个共面点的坐标,并且按照特定的顺序排列
-
SOLVEPNP_DLS (未实现) A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP 实际调用 SOLVEPNP_EPNP
-
SOLVEPNP_UPLP (未实现) Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation 实际调用 SOLVEPNP_EPNP
rotation vectors
姿态解析方法返回的旋转向量,事实上是轴角的形式描述该旋转。
旋转向量是一个三维向量,它通过以下方式描述旋转:
- 旋转轴:旋转向量的方向表示旋转轴的方向。旋转轴是经过原点的直线,物体绕这条直线旋转。
- 旋转角度:旋转向量的模长(长度)表示旋转的角度(以弧度为单位)。旋转角度的大小与旋转向量的长度成正比。
旋转向量与旋转矩阵的转换
旋转向量可以通过罗德里格斯公式(Rodrigues’ formula)转换为旋转矩阵。旋转矩阵是一个3x3的正交矩阵,它直接表示三维空间中的旋转。
在OpenCV中,可以使用以下函数进行转换:
Rodrigues(rotation_vector, rotation_matrix):将旋转向量转换为旋转矩阵。Rodrigues(rotation_matrix, rotation_vector):将旋转矩阵转换为旋转向量。
solveP3P()
solveP3P() 的输入是 3 组 3d-2d 对应点,定义如下:
1 | |
关键结果说明
**旋转向量 (rvec)**
- 物理意义:
表示将物体坐标系(如标定板坐标系)中的点转换到相机坐标系时所需的旋转变换。
具体来说,rvec描述了物体坐标系相对于相机坐标系的旋转姿态。 - 数学形式:
- 旋转向量是轴角表示法(Axis-Angle)的紧凑形式(3×1 向量),可通过 Rodrigues 公式转换为旋转矩阵:
$𝑅=cv2.Rodrigues(𝑟𝑣𝑒𝑐)$ - 矩阵 $𝑅$ 的物理意义为:将物体坐标系下的坐标旋转到相机坐标系下。
- 旋转向量是轴角表示法(Axis-Angle)的紧凑形式(3×1 向量),可通过 Rodrigues 公式转换为旋转矩阵:
**平移向量 (tvec)**
-
物理意义:
表示物体坐标系原点在相机坐标系下的位置偏移量。例如,若标定板坐标系的中心在世界坐标系下为原点,则
tvec是该原点在相机坐标系中的坐标值。 -
数学形式:
- 平移向量是一个 3×1 的向量,单位为毫米(mm)或米(m),需与标定板 3D 点坐标单位一致。
solvePnP() 和 solvePnPGeneric()
solvePnP() 实际上调用的是 solvePnPGeneric(),内部实现如下:
1 | |
solvePnPGeneric() 除了求解相机位姿外,还可得到重投影误差,其定义如下:
1 | |
solvePnPRansac()
solvePnP() 的一个缺点是鲁棒性不强,对异常点敏感,这在相机标定中问题不大,因为标定板的图案已知,并且特征提取较为稳定
然而,当相机拍摄实际物体时,因为特征难以稳定提取,会出现一些异常点,导致位姿估计的不准,因此,需要一种处理异常点的方法
RANSAC 便是一种高效剔除异常点的方法,对应 solvePnPRansac(),它是一个重载函数,共有 2 种参数形式,第 1 种形式如下:
1 | |
solvePnPRefineLM() 和 solvePnPRefineVVS()
OpenCV 中还有 2 个位姿细化函数:通过迭代不断减小重投影误差,从而求得最佳位姿,solvePnPRefineLM() 使用 L-M 算法,solvePnPRefineVVS() 则用虚拟视觉伺服 (Virtual Visual Servoing)
solvePnPRefineLM() 的定义如下:
1 | |
应用实例
位姿估计 (静态+标定板)
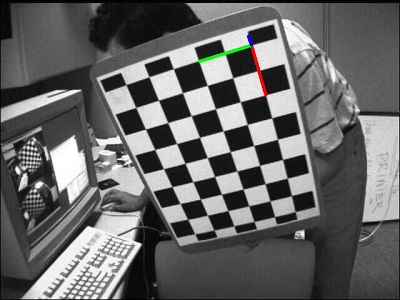
当手持标定板旋转不同角度时,利用相机内参 + solvePnP(),便可求出相机相对标定板的位姿
1 | |
当标定板旋转不同角度时,相机所对应的位姿如下:


参考资料
- https://www.cnblogs.com/xinxue/p/15189486.html
- OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction / Pose Estimation
- OpenCV Tutorials / Camera calibration and 3D reconstruction (calib3d module) / Real time pose estimation of a textured object
文章链接:
https://www.zywvvd.com/notes/study/camera-imaging/pnp/pnp/
“觉得不错的话,给点打赏吧 ୧(๑•̀⌄•́๑)૭”

微信支付
支付宝支付